Creating a new identity, a sense of self, happens at times in our lives, usually after a significant life event. For me, becoming a widow was one such event.
No longer was I a wife or carer. I was a widow, determined to forge a new sense of self as a “merry widow”.
I settled on the “merry travelling widow”. Let me tell you, I got moving on that. What I had planned:
May 2020, multi-modal trip to Melbourne and back on trains, plains, and ships.
November 2020, camp and cruise from Cairns to Bamaga and back.
April 2021, New Zealand by rail and ferry, flying in, cruising back.
September 2021, a Queensland cruise.
May 2022, a half world cruise, Brisbane to Southhampton, train to France, 8 weeks there, then the Orient Express from Paris to Venice, overland to Rome, then flying home. It was to be a glorious three month indulgence.
But, we all know what happened in February, 2020. Covid-19. All those travel plans got cancelled.
Who was I?
If I couldn’t be the “merry travelling widow”, then who was I? That’s when I settled on the “merry student widow”, as going to university had been a lifelong dream.
Prerequisites. I met the prerequisites from life experience, but I was apprehensive about writing, and, let’s face it, I left school in 1988.
I found UQ College and their Tertiary Preparation Program. Back then, in 2020, it was free. It was a crazy but wonderful program that crammed Year 11 into 13 weeks, and then crammed Year 12 into another 13 weeks.
It was wonderful. All mature age students, small class sizes, because of Covid-19, on campus at the University of Queensland’s magnificent St Lucia campus. I did Academic English, Maths, Chemistry, Biology, and Business Management.
I loved it. I thrived. It was amazing. It was life-changing. I was happy.
Regrettably, university turned out to be a major disappointment. Yes, my undiagnosed autism, and the trials and tribulations of being a grey-haired mature-age student played into it, as well. Imposter syndrome occupied every thought.
Back to UQ College
This is an essay I wrote for Chemistry. From the list of topics, I chose:
Topic Number and Name: 6. The quality of air in towns and cities is greatly affected by automobile emissions. What causes this pollution and what can be done to control it? How does the “catalytic converter” help to cut down on the pollutants released from car exhausts? Discuss the chemistry of automobile emissions and why they are pollutants and the chemistry behind the catalytic converter.
This was a no-brainer for me. With my background in occupational health and safety and environmental management, 11 years of that in downstream petroleum, along with a lifetime of “leaning left and bleeding green”, I knew this like the back of my hand.
So enjoy a technical look into vehicle emissions public health and air quality. Or, as I put it:
A story about cars,
lunatics, acid rain, white
bread, suicide prevention,
and it’s as serious as a
heart attack
(Apologies about the academic language. These assignments were supposed to get us ready for university. Oh, and I got 100% for this. )
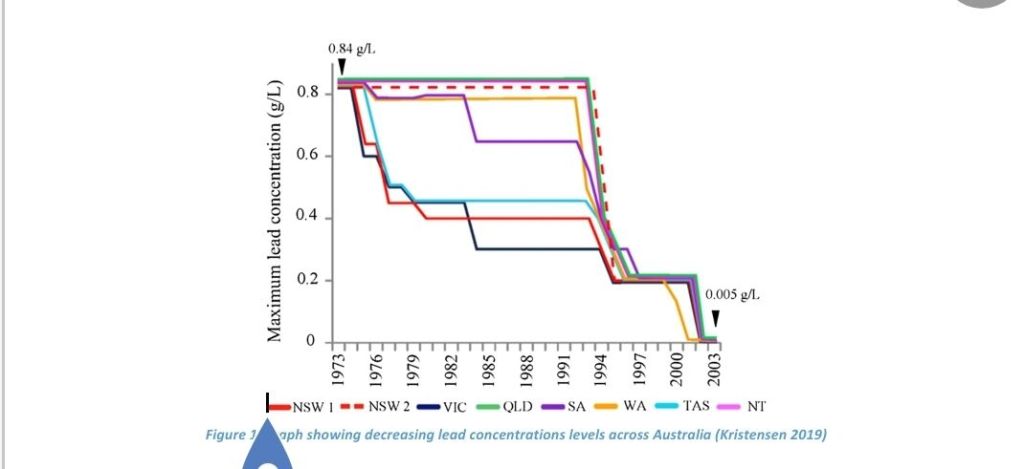
The quality of air in towns and cities is greatly affected by automobile emissions. Vehicle emissions, and industrial emissions, have been linked to acid rain and other pollution events, and the presence of lead in petroleum (gasoline) has been linked to neuropsychiatric illnesses and lead toxicity in the general population (World Health Organisation 2002). Concerns over the air quality around the world saw international efforts to reduce exhaust emissions. In 1975, the USA implemented legislation requiring a 75% reduction in exhaust emissions, which saw the removal of lead from gasoline and gave impetus to the introduction of catalytic converters. In Australia, unleaded gasoline was introduced nationally in 1985, although it had a slow take-up (Kristensen 2015).
Removing lead from gasoline was a major advance in improving air quality in towns and cities (see figure 1 below), and the introduction of catalytic converters for gasoline vehicles also saw significant reduction in air pollution. In more recent times, the introduction of selective catalytic reduction (SCR) for diesel vehicles aimed to reduce greenhouse gas emissions. Internationally, vehicle emissions standards have grown increasingly stringent, such as the current Euro 6 standards and proposed Euro 7 standards. This paper will investigate, firstly, the removal of lead from gasoline; secondly, chemical reactions in a catalytic converter; thirdly, it will investigate the potential loss of functionality in catalytic converters, and lastly, it will explore selective catalytic reduction in diesel vehicles. This investigation of changes resulting in improved air quality begins with the removal of lead from gasoline.
Leaded petrol
Lead was added to gasoline in the 1920s as an anti-knock agent and octane booster, reducing pre-ignition in engines (Compound Interest 2016). Following on from the UN’s 1972 Conference on Human Health and the Environment and the introduction of US EPA standards, lead was removed from gasoline around the world from the mid-1970s (Encyclopaedia Britannica 2019). The release of harmful lead oxides into the atmosphere was as a result of this reaction, in the combustion of leaded gasoline in internal combustion engines.
(CH3CH2)4Pb + 13O2+ heat → 8CO2 + 10H2O + Pb
Lead could then oxidise further to yield as lead(II) oxide:
2Pb + 2O2 → 2PbO2
Removing lead removed lead oxide from vehicle exhaust gases; with the move to unleaded gasoline, the combustion reaction changed to:
C8H18 + 25/2 O2 → 8CO2 + 9H20
Unleaded petrol and catalytic converters
The removal of lead also allowed for the introduction of catalytic converters, to further modify the profile of vehicle exhaust gases (Chemistry LibreTexts 2021). While the reactions above state oxygen as a reactant, the actual fuel/air mixture for the internal combustion engine cycle is drawn from air; air generally consists of 21% oxygen, 78% nitrogen, and the remaining 1% is a mixture of carbon dioxide and other gases. As a result, the reaction that produces nitrogen oxides in vehicle exhaust gases is incidental to the internal combustion engine process. These harmful nitrogen oxides, along with carbon monoxide, are dealt with by the catalytic converter. The catalysts, platinum, palladium and rhodium, trigger a two-stage reaction. The first stage in a catalytic converter deals with the nitrogen oxides, in a reduction reaction, using rhodium as the catalyst.
2NOx → xN2 + xO2
The second stage in a catalytic converter is an oxidation reaction, with platinum and palladium as the catalysts, combining carbon monoxide and oxygen to create carbon dioxide, and combustion of gasoline to produce carbon dioxide and water in vehicle exhaust gases.
2CO + O2 → 2CO2
2C8H18 + 25O2 → 16CO2 + 18H2O
The question remains, though, for how long does a catalytic converter remain effective?
Precious metals found where?
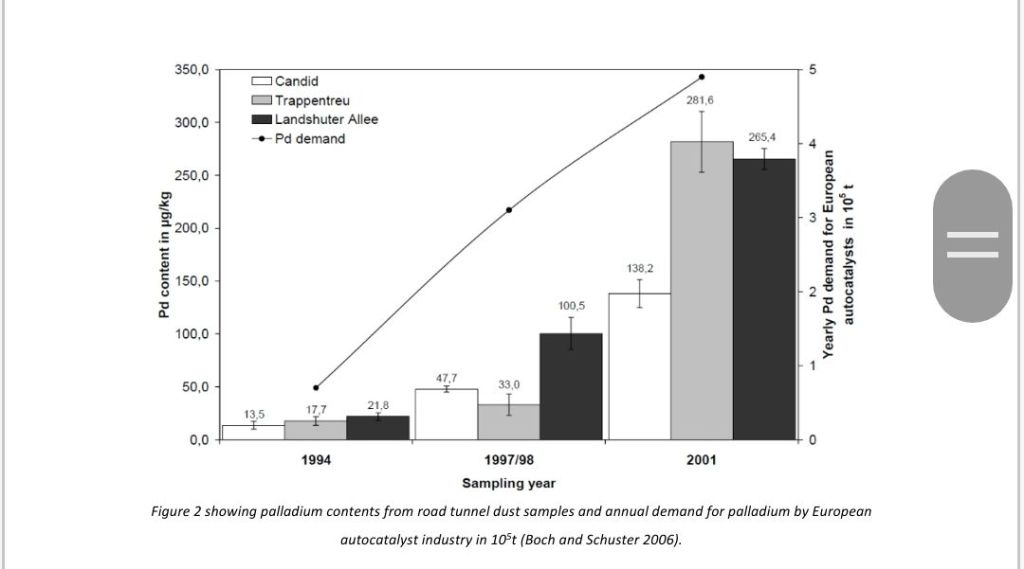
Since the introduction of catalytic converters, researchers have explored the presence of platinum, palladium and rhodium in the environment. Researchers have discovered these precious metals in road sludge and sewage systems. In Germany, a longitudinal study of samples of road tunnel dust, over seven years from 1994 to 2001, showed the presence of palladium in dust samples increasing over time; in 2001, samples yielded a combined total palladium content from the three tunnels involved in the study, of 685.2 palladium μg/kg (Boch and Schuster 2006). See figure 2 below.
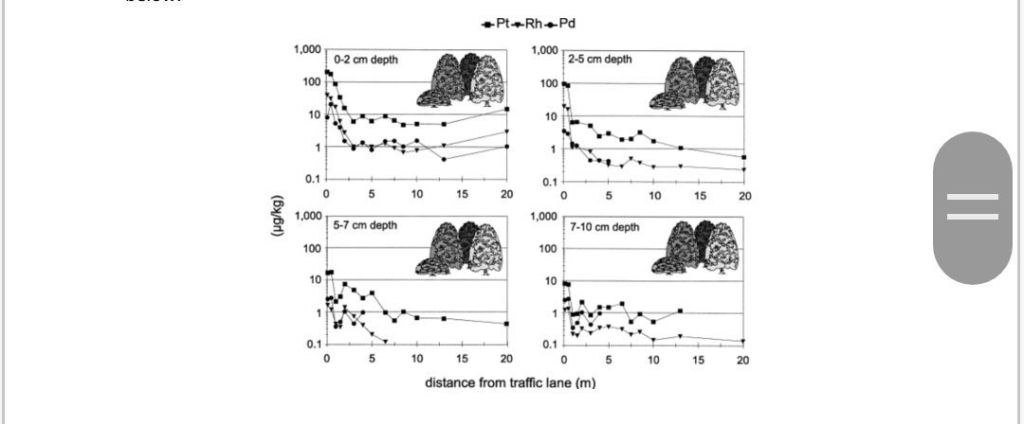
In 1998, further research found platinum, palladium and rhodium at locations along German roads, yielding concentrations above background levels at varying depths, with the highest concentrations found within 10 metres of the road (Schäfer and Puchelt). See figure 3 below.
In 2016, Chinese researchers found platinum, palladium and rhodium above background levels, with a median measurement of 68.25ng/kg, 93.15ng/kg and 23.85ng/kg, respectively (Zhong et al).
The conclusion is that these metals are on the road after having become detached from the catalytic converter (Boch and Schuster 2020; Schäfer et al 1996). In 2019, Goodman et al reported that while car manufacturers, in the expectation that metal atoms would move to form larger particles, usually apply more platinum, palladium and rhodium to catalytic converters than would normally be considered necessary. It was expected that this sintering, forming larger particles would decrease the effectiveness of catalytic converters over time. Goodman et al discovered that the opposite also happens, with the elements becoming ineffective as catalysts, as they decompose into single atoms. This then calls into question the long-term effectiveness of catalytic converters, in the absence of mandatory exhaust emission testing. However, Brisbane City Council offers exhaust emission testing for diesel vehicles as part of the City’s environmental management program (Brisbane City Council 2020).
Diesel fuel
Diesel vehicles have a different profile for exhaust gases, including sulphur dioxide and nitrogen oxides. Sulphur dioxide emissions have been reduced through fuel quality standards in Australia, which restrict sulphur content in diesel to no more than 10mg/kg (Fuel Quality Standards (Automotive Diesel) Determination 2019 (Cwth)). Nitrogen oxides in diesel exhaust gases have been reduced through the introduction of SCR. SCR, aqueous urea, is marketed in Australia as AdBlue, and most modern diesel trucks, and some diesel passenger vehicles, will not operate without an adequate volume of AdBlue in the tank. The SCR is injected into the exhaust of diesel vehicles. See figure 4 below.

The aqueous urea (32.5% in solution) decomposes in the hot exhaust gas to form ammonia and isocyanic acid.
(NH2)2CO → NH3+ HNCO
The isocyanic acid hydrolyses to produce carbon dioxide and ammonia.
HNCO + H2O → NH3 + CO2
Ammonia then reduces nitrogen oxides.
2NO + NH3 + ½O2 → 2N2 + 3H2O and
3NO2 + 4HN3 → 7/2N2 + 6H2O
SCR technology has progressively been rolled out to trucks and passenger vehicles, under the Euro Diesel 6 standard (Association for Emission Control by Catalyst 2021). The ongoing focus on particulate matter in diesel exhausts and the impact on human health, though, has seen a trend to ban diesel vehicles from roads entirely (European Federation for Transport and Environment 2018).
Vehicle exhaust gases, from both gasoline and diesel vehicles, have contributed to air pollution. The switch from leaded gasoline to unleaded gasoline was a major first step; the introduction of catalytic converters for gasoline-powered vehicles saw further improvement. The presence of the catalysts, platinum, palladium and rhodium, in roadside environs, raises questions about the ongoing effectiveness of catalytic converters, in the absence of mandatory testing of vehicle exhaust gases. Exhaust gases from diesel vehicles have also been cleaned up, with aqueous urea as the catalyst to remove greenhouse gases from diesel vehicle exhaust gases.
As the world considers the transition to electric vehicles, and hydrogen powered vehicles, gasoline and diesel-powered vehicles are likely to remain on our roads for several years to come. In the interim, mandatory testing of exhaust emissions in gasoline vehicles could quantify the issue of non-functional catalytic converters, complemented by further research to follow on from the work of Goodman et al.
Diesel vehicle exhaust emissions could also be tested regularly, for particulate matter. Shifting the transport of freight from road to rail, such as is proposed for the inland rail corridor, could see a reduction in the number of trucks on the roads, and there are already many electric buses on the roads. Lessons can be learned from the introduction of tetraethyllead into gasoline, given the public health epidemic that ensued. Such advancements in improving air quality may yield better health outcomes not just for humans, but also our planet.
Reference List
Bannon, E 2018, ‘More cities get tough on diesel’, European Federation for Transport and Environment, viewed 4 February 2021, https://www.transportenvironment.org/news/more-cities-get-tough-diesel,
Boch K, Schuster M, 2006, ‘Determination of palladium in road dust and sewage sludge ashes’, in F Zereini, F Alt (eds), Palladium Emissions in the Environment, Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg, pp. 191-201, https://doi-org.ezproxy.library.uq.edu.au/10.1007/3-540-29220-9_14.
Goodman, ED, Johnston-Peck, AC, Dietze, EM, Wrasman, CJ, Hoffman, AS, Abild-Pedersen, F, Bare, SR, Plessow, PN & Cargnello, M 2019, ‘Catalyst deactivation via decomposition into single atoms and the role of metal loading’, Nature Catalysis, vol. 2, no. 9, pp. 748-755, https://www-nature-com.ezproxy.library.uq.edu.au/articles/s41929-019-0328-1.
Greim, H 2019, ‘Diesel engine emissions: are they no longer tolerable?’ Archives of Toxicology, vol. 93, pp. 2483–2490, https://doi-org.ezproxy.library.uq.edu.au/10.1007/s00204-019-02531-5.
How you can contribute to clean air 2020, viewed 19 January 2021, Brisbane City Council, Brisbane, https://www.brisbane.qld.gov.au/clean-and-green/natural-environment-and-water/air-quality/types-of-pollution.
Kahlon, A & Tang, T, 2021, 7.1: Catalytic Converters, LibreTexts, viewed 4 February 2021, https://chem.libretexts.org/Bookshelves/Physical_and_Theoretical_Chemistry_Textbook_Maps/Supplemental_Modules_(Physical_and_Theoretical_Chemistry)/Kinetics/07%3A_Case_Studies-_Kinetics/7.01%3A_Catalytic_Converters.
Kristensen, LJ 2015,’ Quantification of atmospheric lead emissions from 70 years of leaded petrol consumption in Australia’, Atmospheric Environment, vol. 111, pp 195-291, https://www-sciencedirect-com.ezproxy.library.uq.edu.au/science/article/pii/S1352231015300157.
Landrigan, P 2002, ‘The worldwide problem of lead in petrol’, Bulletin of the World Health Organization, vol. 80, no. 10, p. 768, https://www.who.int/bulletin/archives/80(10)768.pdf?ua=1.
Schäfer, J & Puchelt, H, ‘Platinum-Group-Metals (PGM) Emitted from Automobile Catalytic Converters and Their Distribution in Roadside Soils’, Journal of Geochemical Exploration, vol. 4, no. 1, pp. 307–14, https://doi.org/10.1016/S0375-6742(98)00040-5.
Schäfer, J, Eckhardt, J, Detlef, B, Zsolt, A & Stüben, D 1999, ‘Time-dependent increase of traffic-emitted platinum-group elements (PGE) in different environmental compartments’, Environmental Science & Technology, vol. 33, no. 18, pp. 3166–3170, https://pubs-acs-org.ezproxy.library.uq.edu.au/doi/abs/10.1021/es990033i.
The Chemistry of Petrol & The Tetraethyl Lead Story 2016, viewed 4 February 2021, Compound Interest, Cambridge, https://www.compoundchem.com/2016/05/17/petrol/.
Upcoming Euro 7 emission regulations to drive Europe’s zero-emission mobility goal, 2021, Association for Emission Control by Catalyst, Belgium, viewed 4 February 2021, https://dieselinformation.aecc.eu/upcoming-euro-7-emission-regulations-to-drive-europes-zero-emission-mobility-goal/#:~:text=The%20new%20Euro%207%20standards,vehicles%20during%20their%20daily%20use.&text=For%20instance%2C%20petrol%20cars%20are,are%20allowed%20from%20diesel%20vehicles.
What is AdBlue/DEF – The chemistry?, n.d., viewed 19 January 2021, Ad Blue Dispensing, Wiltshire, http://www.adbluedispensing.co.uk/adblue-def-guide/.
What Really is AdBlue?, n.d., viewed 19 January 2021, Ad Blue Dispensing, Wiltshire, http://www.adbluedispensing.co.uk/what-really-is-adblue/
Zhong, L, Li, J, Yan, W, Tu, X, Huang, W & Zhang, X, ‘Platinum-group and other traffic-related heavy metal contamination in road sediment’, Journal of soils and sediments, vol. 12, no. 6, pp.942–951, https://doi-org.ezproxy.library.uq.edu.au/10.1007/s11368-012-0527-8.
Legislation
Fuel Quality Standards (Automotive Diesel) Determination 2019 (Cwth)
